In the field of fundamental machine learning theory, the convergence analysis of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) has always been a core research topic. Most existing studies are based on the assumption of sample independence; however, data in real-world scenarios often exhibits complex dependency structures, such as in speech recognition, financial prediction, and time series analysis. To address this challenge, a team led by Yueyang Men from Beijing University of Chemical Technology collaborated with a team led by Yongli Xu from Beijing University of Technology to propose, for the first time, a theoretical framework for fast learning rates of DNNs based on Geometrically Strongly Mixing Sequences. This work provides theoretical support for deep learning algorithms under non-independent smples. The findings have been published in IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, a top-tier journal in the field of artificial intelligence.
Background and Challenges
Traditional theoretical analyses typically assume sample independence, but practical data (e.g., time series, sensor network data) often shows complex dependencies. Mixing sequences are important tools for characterizing dependencies; however, research integrating them with deep learning has long been scarce. The core scientific question addressed in this paper is: "Under conditions of non-independent data, do the convergence conclusions for DNNs still hold?"
Core Methods and Innovations
This study focuses on DNN regression problems, assuming the sample sequence satisfies geometric strong mixing properties, and conducts an error analysis for the DNN regression algorithm based on Empirical Risk Minimization (ERM). Unlike the independent sample scenario, under the mixing sequence setting, the algorithm's learning performance is no longer determined solely by the sample size but is dominated by the "effective number of observations." By skillfully applying mixing probability inequalities, the research team provided precise estimates for the sample error. Combined with existing analyses of DNN approximation error, they ultimately established a fast convergence rate for DNN regression under geometrically strongly mixing sequences. When the key parameters of the mixing sequence tend to infinity, this convergence rate reduces to the rate achievable under independent samples, demonstrating the natural generalizability of the theoretical results.
Experimental Validation
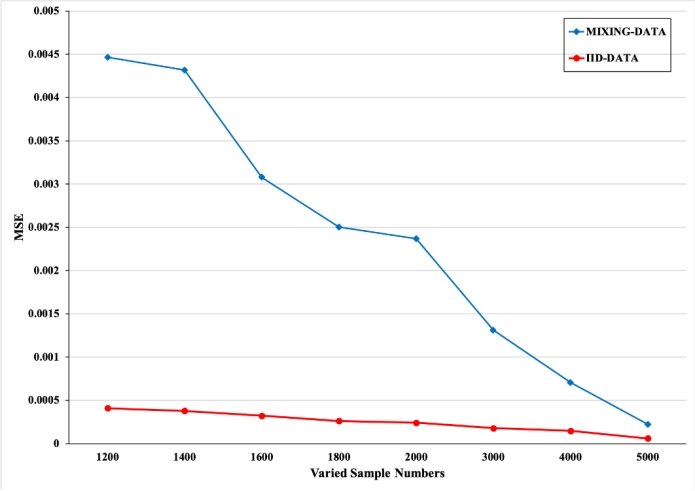
To validate the theoretical findings, the team designed a series of numerical experiments. They generated datasets with geometric strong mixing properties using Autoregressive (AR) models and employed the Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) method to approximately solve the ERM problem, obtaining the prediction function. Experiments compared the learning performance under non-independent data versus independent data. The results showed that, with the same number of training samples, the error obtained using the non-independent data generated by the AR model was larger than that for independent data. However, as the sample size increased, the gap between the errors gradually narrowed, consistent with the theoretical analysis.
Article Information
Yueyang Men, Liang Li, Ziqing Hu, et al. Learning Rates of Deep Nets for Geometrically Strongly Mixing Sequence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2025, 36(3): 5826-5832.
DOI: 10.1109/TNNLS.2024.3371025
About the Journal
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems is a leading international journal in the field of artificial intelligence. It focuses on cutting-edge theories and methods in neural networks and learning systems, covering important research directions such as deep learning and reinforcement learning.
